How to Check Your Browser Engine Version: Most Practical Detection Methods (2026 Updated)
Many people, when using a browser, usually only care about whether the interface looks good or if the features are sufficient, and rarely pay attention to the browser's engine version.
In fact, the engine version is the key factor that truly determines the browser's security, stability, and ability to smoothly pass various risk control checks.
Accurately understanding which engine version your browser is using can help you better assess whether your current environment is safe and reliable, and also avoid unexpected issues.
1. Why You ShouldCheck Your Browser Engine Version
A browser engine (rendering engine) is the core component responsible for parsing web pages, executing scripts, and providing security isolation. Common engines include:
• Blink (Chrome, new Edge, Opera, etc.)
• Gecko (Firefox)
• WebKit (Safari)
Even the same browser can have significant differences in security across different versions; in practice, you may also encounter situations where the browser is disguised or the User-Agent has been tampered with.
Continuing to use an old engine means some known vulnerabilities remain unpatched, amplifying security risks. In scenarios like account risk control, anti-cheating, and compatibility checks, the browser engine version itself becomes a key criterion.
2. Methods to Check Browser Engine
Method 1: Built-in Browser Information
The most common approach is to view the version information via the browser's "About" page, for example:
• Chrome: Settings → About Chrome
• Edge: Settings → About Microsoft Edge
• Firefox: Help → About Firefox
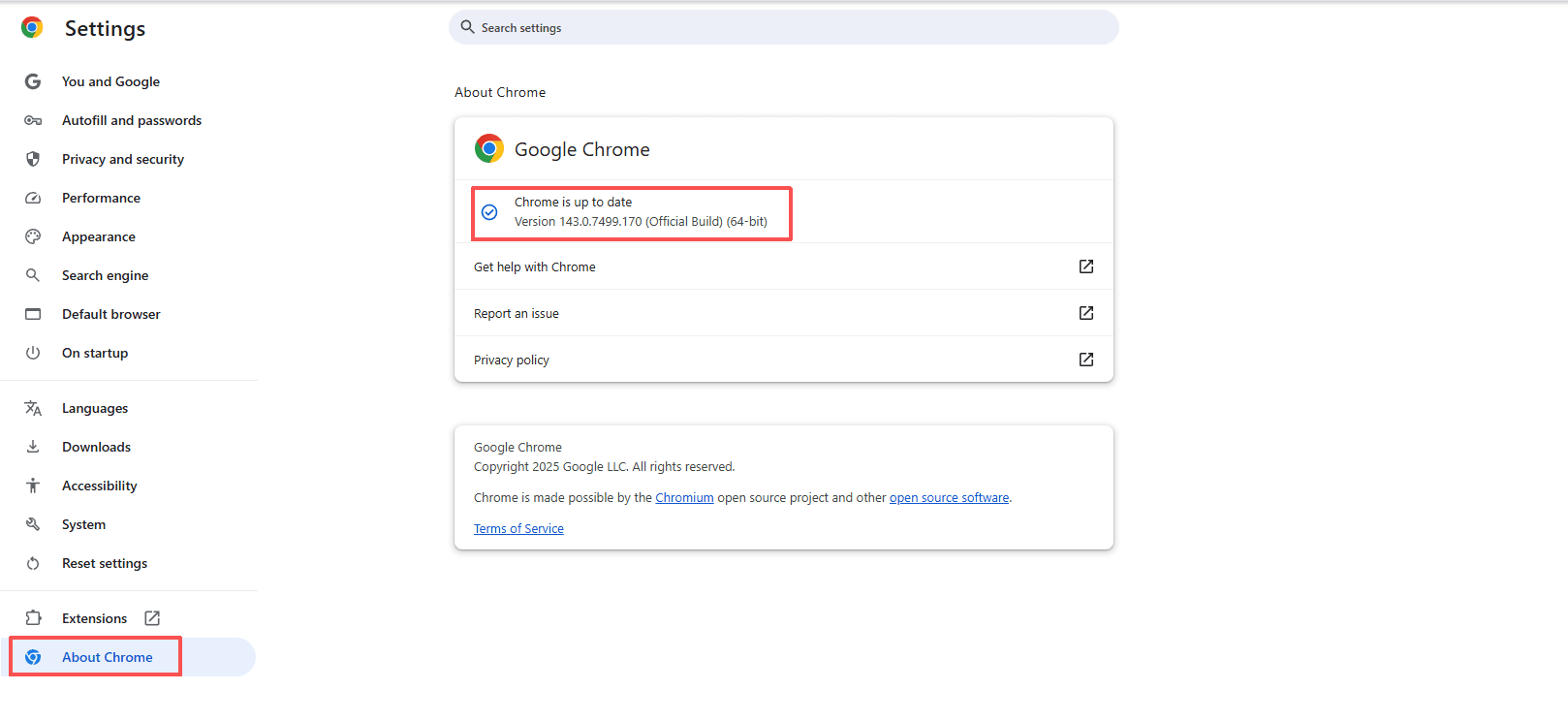
Advantage: Simple operation, suitable for ordinary users to quickly check.
However, disadvantages are also obvious:
Only the browser version number can be seen
• Cannot verify if the engine is disguised
• Cannot determine if the UA matches the real environment
• Limited value for testing, risk control, and technical scenarios
Method 2: Check User-Agent
Using developer tools or online UA lookup sites, you can see the User-Agent string returned by the browser and infer the engine type and version.
For example, Blink and Gecko are usually indicated in the UA.
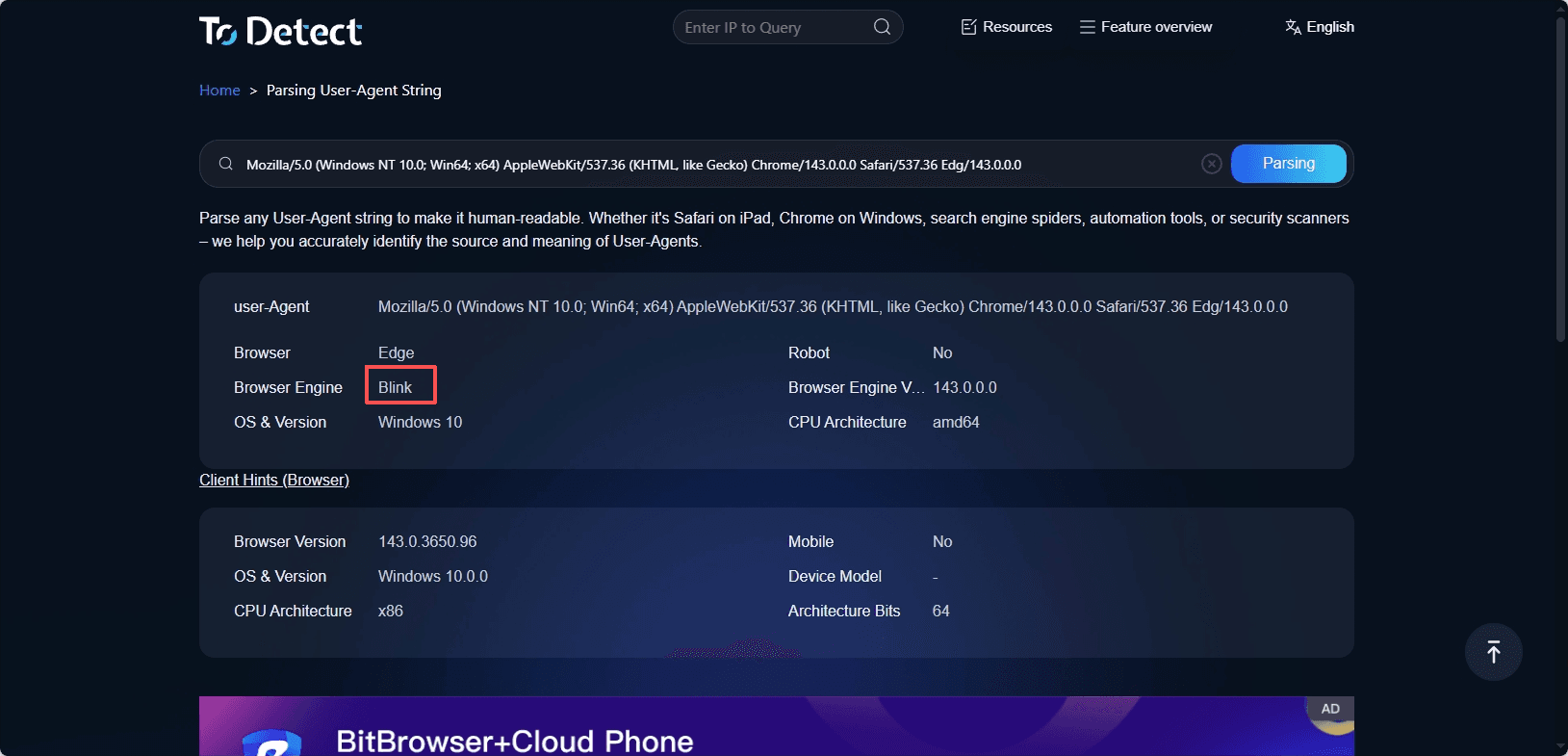
However, User-Agent is one of the fields most easily modified or disguised, and it should only be used as reference information, not as evidence of the browser engine's authenticity.
Method 3: Use an Online Browser Engine Version Detection Tool
Professional browser detection tools use multiple low-level characteristics to comprehensively determine the browser engine and version.
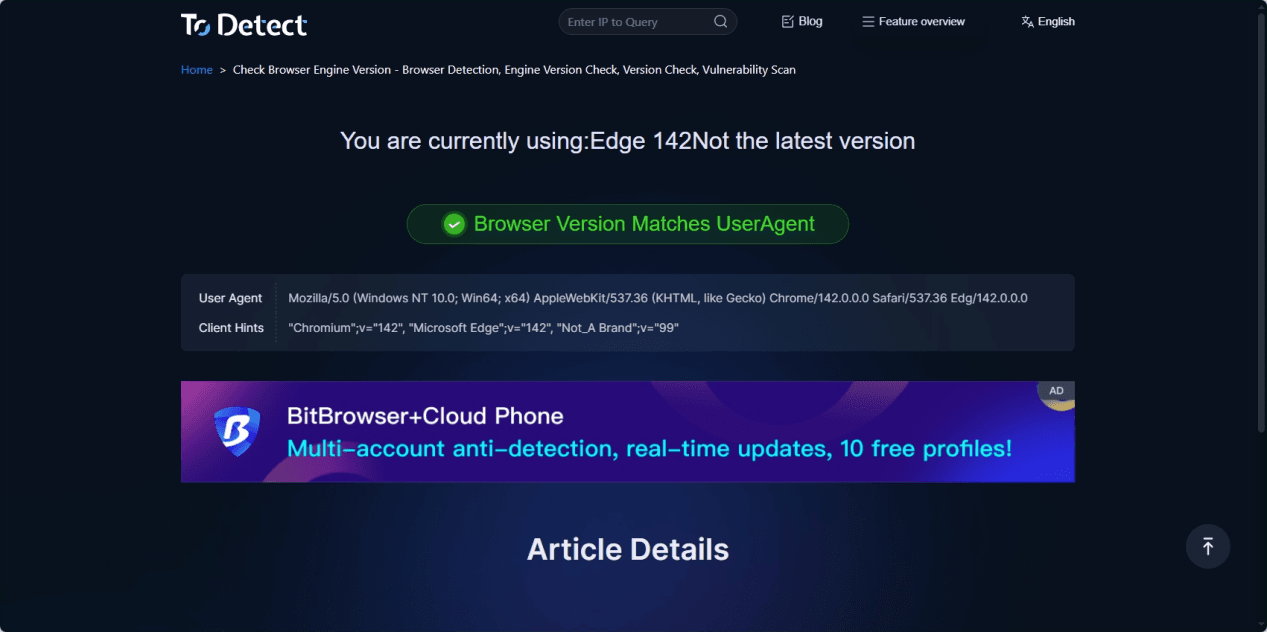
ToDetect's browser engine version detection does not rely solely on the User-Agent but combines the browser's low-level behavior and environmental characteristics for a comprehensive identification.
With ToDetect, you can quickly obtain:
• The actual engine version of the current browser
• The compatibility between the browser and operating system
• Whether there are obvious disguises or abnormal features
The entire process requires no plugin installation or manual operation — just open the page and detection is completed automatically.
Scenarios Where ToDetect Is Useful
1. Verify if the browser's displayed information matches the real environment
Some environments may display as Chrome, but the underlying behavior does not match Blink engine characteristics. ToDetect helps quickly identify such inconsistencies.
2. Confirm if the engine version is outdated
Older engine versions not only have security vulnerabilities but may also cause web compatibility issues.
ToDetect's version identification capability helps determine whether you need to update or replace the environment.
Conclusion
Differences in browser engine versions directly affect browser behavior and security performance.
By accurately detecting the engine version, you can better understand the true state of your environment and avoid potential issues caused by inconsistent information.
Properly using detection tools helps achieve a more stable and trustworthy browsing experience in complex network environments.
FAQ
1. Do engine version detection tools affect privacy?
Most detection tools only collect basic browser environment information and do not involve personal data, but specifics depend on the tool.
2. How can engine version information help solve browser issues?
It helps diagnose page display errors, script errors, or compatibility problems.
3. Will updating the browser engine affect installed plugins?
Engine updates can sometimes cause certain plugins to be incompatible and require plugin developers to provide updates.
 AD
AD

