How to Check Browser Fingerprint Security and Fix Detection Issues
This situation usually indicates that the fingerprint information generated by the browser differs from the actual hardware or system parameters of the device.
The purpose of browser fingerprint detection is to help users understand whether the current environmental characteristics are consistent and whether there is a reasonable camouflage effect.
The following content will introduce how to conduct detection, the tools that can be used, and common reasons and adjustment methods for abnormal detection results.

The meaning of browser fingerprint.
Browser fingerprinting is a set of information used to identify a device. When users visit a website, several parameters of the browser and system are collected. These parameters include operating system version, browser type, fonts, resolution, plugin list, time zone, language settings, audio features, WebGL rendering data, and so on.
The combination of this data can form a unique identification code. Even if you clear cookies or use privacy mode, the website can still determine whether it is the same user through these features.
Fingerprinting can reflect whether the browser environment is consistent and spoofable. When the detection results are abnormal, it indicates that there is an unreasonable difference between certain parameters.
II. How to determine if a browser fingerprint is secure
To determine whether a browser fingerprint is secure, it mainly depends on whether the generated environmental information is consistent, complete, and not easily identified as an abnormal configuration.
The process of fingerprint detection is not about assessing whether a certain browser is "good" or "bad," but rather understanding how natural the browser appears to a website or platform by comparing parameters.
A secure browser fingerprint has the following characteristics:
The system, language, time zone, and network IP region are consistent.
The browser version is normal and shows no signs of forgery.
There is no significant deviation in hardware fingerprint detection such as Canvas, WebGL, and Audio.
The font and plugin list matches the system environment;
The User-Agent field corresponds to the browser kernel.
When these conditions are met, the browser environment is closer to that of a real device. In contrast, if the detection report indicates that some parameters have been modified or confused, it may lead to fingerprint anomalies.
3. RecommendedBrowser fingerprint detection tool
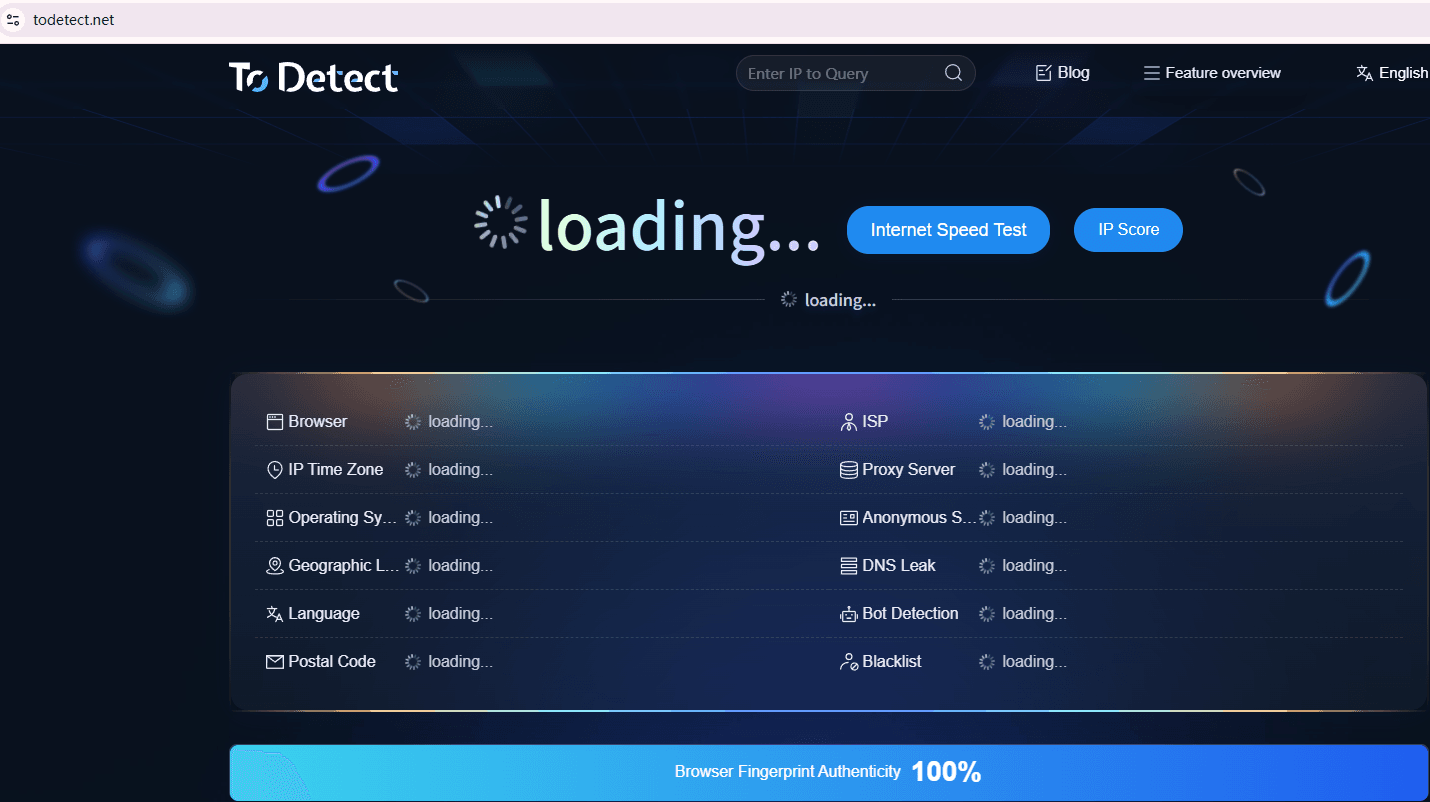
ToDetect browser fingerprint detection tool
This website supports real-time detection of browser fingerprint information. After accessing the page, it automatically generates a report displaying various data such as Canvas, WebGL, Audio, fonts, resolution, language, time zone, and more.
The detection process does not require additional plugins. The page provides a results comparison, highlighting any parameters that show anomalies or inconsistencies. ToDetect demonstrates the fingerprint generation logic through local detection, making it easier for users to identify risk points.
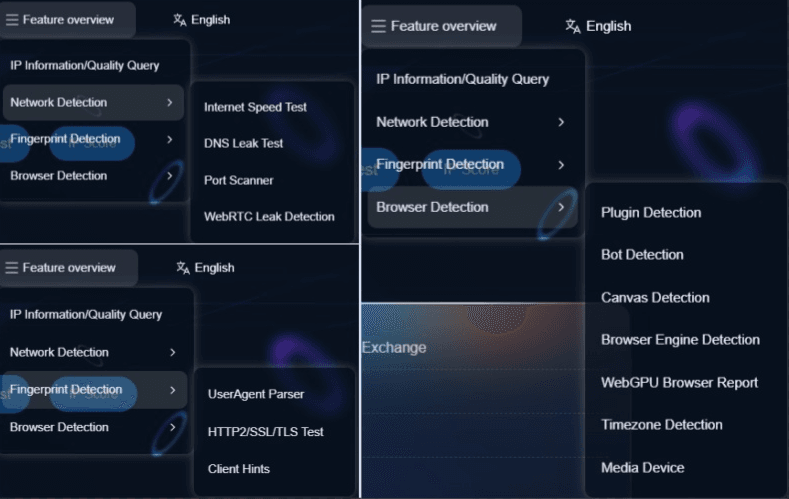
You can click on Feature Overview to view more detailed detection features.
BrowserLeaks
This website displays the information exposed by the browser through different interfaces. The detection content includes network protocols, geolocation interfaces, media device identifiers, etc. It can help analyze all parameters exposed by the browser when accessing websites. The results are relatively detailed, but some item explanations require a certain technical background.

Using two tools for cross-checking can reveal the differences under different detection mechanisms.
Four,Browser fingerprint detection exceptionCommon causes and solutions
The system and browser configurations are inconsistent.
If the time zone does not match the IP location, or the language settings do not match the system region, the detection will show abnormalities. Adjusting the operating system language, time zone, and browser settings to keep them consistent can restore normal status.Graphics rendering parameter exception (Canvas/WebGL)
The GPU spoofing, driver differences, or different browser versions can change the Canvas image hash value. Variations in rendering parameters can lead to abnormal detection results. Updating the GPU driver or using the hardware fingerprint protection feature of the browser can reduce fluctuations.Audio fingerprinting is unstable.
The contextual features of audio depend on the system hardware and drivers. Audio interface spoofing may cause detection results to deviate from the average. Maintaining stable audio device configurations can mitigate anomalies.IP address and browser feature conflict
When the area where the proxy or network node is located does not match the browser language or time zone, it will be detected as an environment inconsistency. Choosing a low-latency, stable residential IP and keeping the regional parameters consistent can reduce risk.Plugins or extensions interference
Some browser extensions may modify UA, fonts, or WebRTC parameters. If the detection report indicates "extension exposure" or "modification traces," you can disable the extensions one by one and retest.Differences in browser versions or kernels
Older versions of browsers may contain deprecated interfaces or rendering features. The detection system will mark these features as anomalies. After upgrading the browser version, a more stable result can be obtained upon retesting.Different algorithms for detection platforms.
The algorithm models of different detection platforms vary, and the criteria for judgment are not completely consistent. Results differences do not necessarily represent real issues. A comparison reference can be made between ToDetect and other browser fingerprint detection tools.
5. How to optimize the browser fingerprint environment
Maintaining consistency between system and browser configurations is a basic operation. Regularly checking the environment can help observe trends in parameter changes. When obvious anomalies occur, first check the proxy and time zone, then look at the Canvas and audio features.
For multiple account operations or cross-regional use, each environment should be kept independent. The reports provided by the ToDetect browser detection tool can clearly display various parameters, which helps assess whether adjustments to the environment are needed.
 AD
AD