IPv4 and IPv6: A Comprehensive Interpretation of Network Addresses
In today’s era of rapid Internet development, IP addresses play a crucial role as the core identifier in network communication. Every device—whether a computer, smartphone, or server—relies on an IP address to identify itself and exchange data with other devices. With the exponential growth of networked devices, the IP addressing system has undergone a transition from IPv4 to IPv6. This article provides a comprehensive explanation of the differences, applications, and development trends of IPv4 and IPv6, and illustrates the practical functions of the ToDetect Browser Fingerprint Detection Tool to help readers understand the concept and real value of network addresses.
What is IPv4?
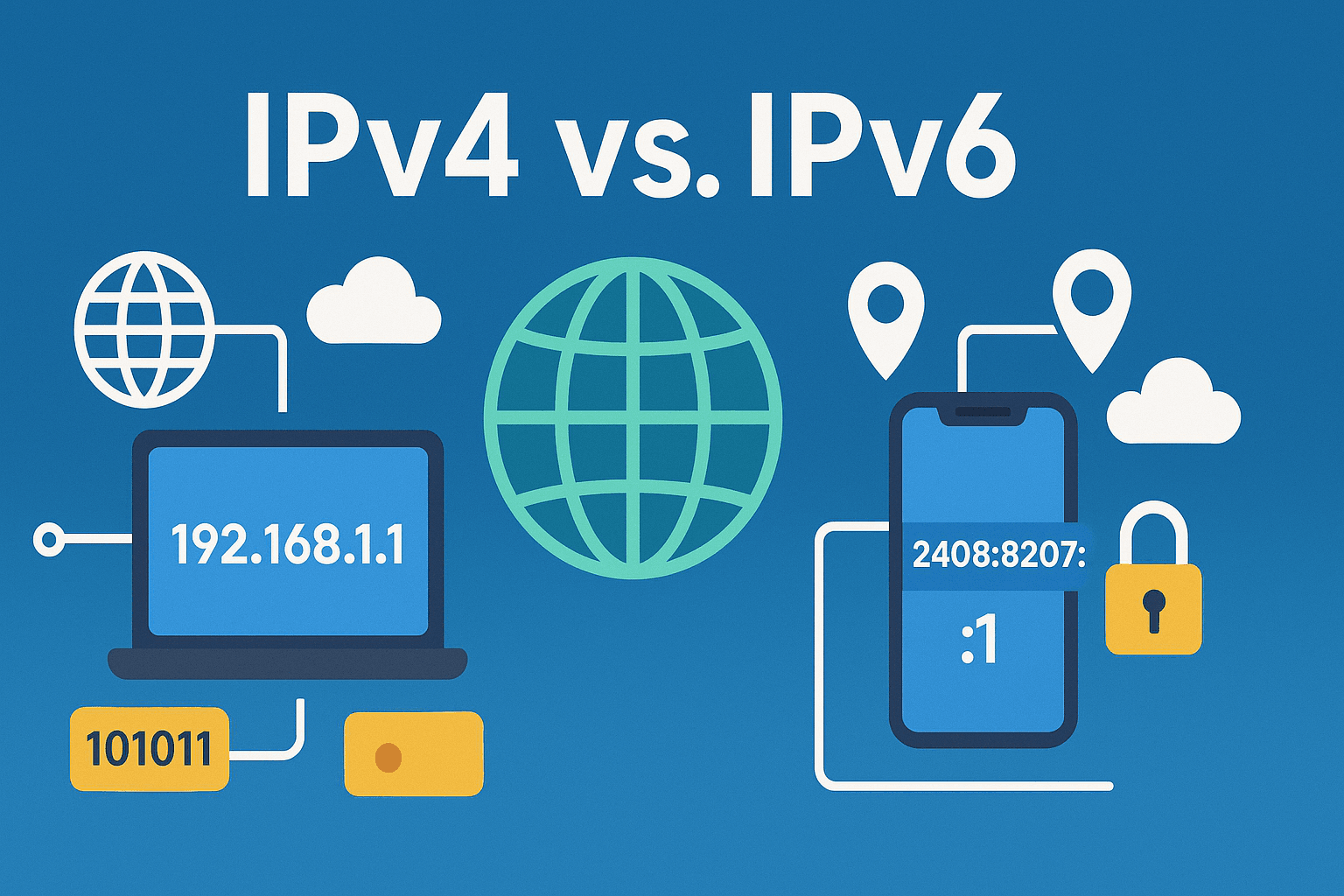
IPv4, or Internet Protocol Version 4, is the most commonly used address format on the internet. It consists of four groups of numbers ranging from 0 to 255, for example, 192.168.1.1. The total number of IPv4 addresses is approximately 4.2 billion, which once supported the development of the global internet.
The characteristics of IPv4 include:
- The address format is simple: composed of four decimal numbers, each separated by a dot.
- Wide application: Almost all network devices, websites, and servers support IPv4.
- Limited Address Space: As the number of devices increases, IPv4 addresses are becoming increasingly scarce, especially in the fields of mobile devices and the Internet of Things.
With the ToDetect browser fingerprint detection tool, you can easily view your device's public IPv4 address and related information, such as geographic location, network operator, and IP type, which is very helpful for daily network management and security monitoring.
The Birth and Advantages of IPv6
With the increasing scarcity of IPv4 address resources, IPv6 has emerged. IPv6 employs a 128-bit address, formatted as 2408:8207:xxxx::1, and can theoretically provide over 3.4×10³⁸ independent addresses, thus addressing the issue of IPv4 address exhaustion.
The main characteristics of IPv6 include:
- The address space is vast: it can almost allocate a unique address for every device.
- More efficient routing: IPv6 simplifies routing table design and improves network transmission efficiency.
- Built-in security features: The protocol design integrates IPSec, supporting data encryption and identity authentication.
- Suitable for mobile internet: capable of meeting the network demands of future 5G, the Internet of Things, and smart devices.
In the ToDetect browser fingerprint detection tool, you can simultaneously detect the device's IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, achieving a comprehensive network information display in a dual-protocol environment. This not only helps users understand the network source but also has important value for debugging network connections and analyzing access security.
The main differences between IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv4 and IPv6 differ not only in address length but also in protocol features, application scenarios, and network management methods. The main differences include:
- Address length: IPv4 is 32 bits, and IPv6 is 128 bits.
- Address representation: IPv4 uses dotted-decimal notation, such as 192.168.0.1; IPv6 uses colon-separated hexadecimal, such as 2408:8207:xxxx::1.
- Number of addresses: Approximately 4.2 billion for IPv4, and nearly unlimited for IPv6.
- Packet header: IPv4 is relatively complex, while IPv6 has a simplified design for higher efficiency.
- Security: IPv4 requires additional configuration for IPSec, while IPv6 natively supports IPSec.
- Network management: IPv4 often relies on NAT technology for address translation, while theoretically, IPv6 does not require NAT, as each device can have its own public IP.
With the ToDetect browser fingerprint detection tool, you can directly see whether your device is using IPv4 or IPv6, and determine if it supports a dual-stack network, providing direct reference for network debugging and security analysis.
Application Scenarios of IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 and IPv6 are widely used in practical networks:
- Daily Internet Use
Most home users still access the internet via IPv4, but an increasing number of ISPs and websites are beginning to support IPv6. IPv6 reduces address conflicts and provides a more stable connection experience. - Enterprise Network and Servers
Enterprise servers commonly use IPv6 to ensure sufficient IP resources and improve data transmission efficiency. This advantage of IPv6 is particularly evident in cloud computing and distributed services. - Mobile Internet and Internet of Things
The number of smart devices, sensors, and wearables is rapidly increasing, and IPv4 can no longer meet the demand. IPv6 can assign a unique address to each device, ensuring smooth communication between devices. - Safety and Protection
IPv6 natively supports IPSec encryption, enhancing the security of data transmission. Combined with the ToDetect browser fingerprinting tool, you can identify the IP type, privacy connection, and network operator, helping assess the security of access.
How to use the ToDetect browser fingerprint detection tool to view IPv4 and IPv6
Using the ToDetect Browser Fingerprint Detection Tool to check IP information is very simple:
- Open the page: https://www.todetect.cn/ip-info/
- The system automatically detects the public IPv4 and IPv6 addresses of the device.
- The page will display detailed information, including public IP, geographical location, network operator, IP type, and privacy connection status.
- Users can also input other IPs for queries to obtain complete network information analysis.
This feature not only allows users to intuitively understand the network status of their devices, but also provides important data support for network management, privacy protection, and security defense.
Promotion of IPv6 and Future Trends
As the number of internet devices continues to grow, IPv6 will become the mainstream of future network development. The main trends include:
- Dual-stack network popularization: More and more devices and ISPs simultaneously support IPv4 and IPv6, enabling seamless switching.
- Comprehensive coverage of the Internet of Things: Smart homes, industrial sensors, and more will rely on unique IPv6 addresses.
- Enhancing network security: IPv6 combined with encryption technology provides a more secure access environment.
- Improve network performance: simplify routing design, reduce latency, and enhance transmission efficiency.
Through the ToDetect browser fingerprint detection tool, you can get real-time information on IPv6 usage, determine whether devices support IPv6, and prepare for future network upgrades.
Summary
IPv4 and IPv6 are essential foundations of Internet communication:
- IPv4: Widely used, limited addresses, suitable for existing network environment.
- IPv6: With almost unlimited addresses, it supports new devices and security features, making it the trend for future network development.
Through the ToDetect Browser Fingerprint Detection Tool, you can easily view information such as IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, geographic location, network provider, and IP type, helping users better understand their network connection, optimize network usage, and enhance online security.